Definition
A differential equation is a equation that contains derivatives and algebraic operations.
Solutions to differential equations are functions, not numbers!
Example
System of differential equations
In that case we say that solution is an ordered pair of functions such that both of these equations simultaneously hold.
Partial differential equations
Solutions would be that satisfy the above equation.
Definition
A differential equation in which there is only one independent variable is called and Ordinary differential equation. If there are more than one independent variable then it is called Partial differential equation.
Definition
Largest number such that th derivative appears in a differential equation is called order of the equation.
is a 3rd order differential equation.
Definition
Suppose that we have a first order ODE with dependent variable and independent variable . Then, a condition of the form is called an initial condition.
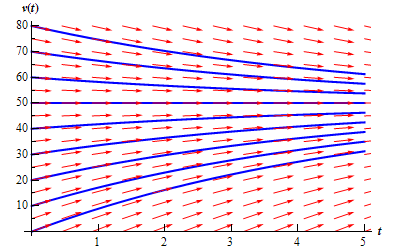
Initially we do not know the solution curve of a differential equation. But we can infer some tangents in the domain. This gives us a approximate graph for the given equation. This tangent graphs are called a direction field like this one:
METU MATH219 Curriculum
- This introduction
- Separable equations
- Homogeneous equations
- Linear equations
- Principle of superposition
- Existence-uniqueness theorems [TO BE]
- Exact equations